Cinnamaldehyde Contact Allergen
Cinnamaldehyde Contact Allergen
This post is about Cinnamaldehyde a skin allergen that can also cause allergic contact stomatitis. Additionally, if consumed in excess, cinnamon can cause other side effects, including liver damage and allergic reactions. Cinnamon has been linked with health benefits . These benefits are improved blood sugar control and lowering of some cardiac risk factors for heart disease.
Where Cinnamon comes from
The inner bark of the Cinnamomum tree provides the source for the spice. The two main types of cinnamon are:
- Cassia: the most common type called “regular” cinnamon.
- Ceylon: Known as “true” cinnamon, Ceylon has a lighter and less bitter taste.
Commonly found in supermarkets, because Cassia cinnamon is much cheaper than Ceylon cinnamon.
What other chemicals are in the Spice
While Cassia cinnamon is safe to eat in small to moderate amounts, eating too much may cause health problems because it contains high amounts of a compound called coumarin. Research has found that eating too much coumarin may harm your liver and increase the risk of cancer.
According to a report in the June 2015 issue of Pharmacognosy Research, people who take warfarin and other blood-thinning medications should exercise caution when consuming cinnamon, as high levels of coumarin in cinnamon interfere with blood clotting in these individuals.
About Cinnamaldehyde allergies
Cinnamaldehyde (CAS Number 1437-10-9), an organic compound with the formula C9H8O. Occurring naturally as predominantly the trans (E) isomer. Furthermore, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. Particularly, it appears in other flavors like Almond, Apricot and Butterscotch. According to a paper published in Clinical Nutrition in April 2019, allergic responses and gastrointestinal symptoms are the most frequent negative consequences of cinnamon ingestion. Therefore cinnamaldehyde is a Standardized Chemical Allergen, therefore care needs to be taken in its use. The physiologic effect of cinnamaldehyde is by means of Increased Histamine Release, and Cell-mediated Immunity.
Cinnameldahyde causes allergic contact stomatitis (sore mouth issues) in sensitized individuals. It is on the contact allergens in humans EU List of fragrance ingredients. Cinnamaldehyde contact allergy causes your skin to react. Consequently when exposed to this substance, it may take several days for the symptoms to appear. Typical symptoms include redness swelling, itching and fluid-filled blisters. In the mouth white patches that look like ulcers. These especially can be extremely uncomfortable. Sensitivity to cinnamaldehyde may be identified with a clinical patch test. Moreover it is found in the Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
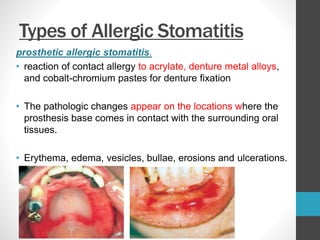
allergic contact stomatitis from Cinnamaldehyde
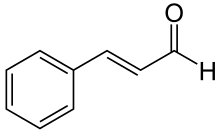
Skeletal formula of Cinnamaldehyde molecule
Other names for Cinnamaldehyde
- Cihinnamaldehyde
- Cinnamal
- Cinnamic aldehyde
- trans-Cinnamaldehyde
- 3-phenyl-2-propenal
- 3-phenylprop-2-enaldehyde
- beta-phenylacrolein
- cinnamic aldehyde
- cinnamic aldehyde, (E)-isomer
- supercinnamaldehyde
- trans-3-phenylprop-2-enaldehyde
- trans-cinnamaldehyde
- Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-Phenylprop-2-enal